Toyota RAV4 (XA40) 2013-2018 Service Manual: A/f sensor circuit slow response (bank 1 sensor 1)
Hint:
Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the three-way catalytic converter (twc) and located near the engine assembly.
Description
Refer to dtc p2195 (see page es-292).

Monitor description
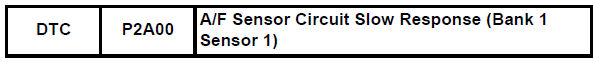
After the engine is warmed up, the ecm performs air-fuel ratio feedback control to maintain the air-fuel ratio at the stoichiometric level. In addition, active a/f control is performed for approximately 10 seconds after the preconditions are met in order to measure the a/f sensor response rate. During active a/f control, the ecm forcibly increases and decreases the injection volume a certain amount, based on the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio learned during normal air-fuel ratio control, and measures the a/f sensor response rate. The ecm receives a signal from the a/f sensor while performing active a/f control and uses it to calculate the a/f sensor response rate deterioration level.
If the a/f sensor response rate deterioration level is less than the threshold, the ecm interprets this as a malfunction and sets the dtc.
Confirmation driving pattern
Hint:
Performing this confirmation pattern will activate the a/f sensor response monitor.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Turn the ignition switch on.
- Turn the tester on.
- Clear dtcs (if set) (see page es-35).
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / monitor info / monitor result.
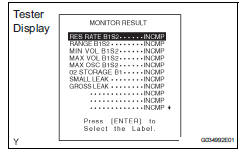
- Check that res rate b1s1 is incomp.
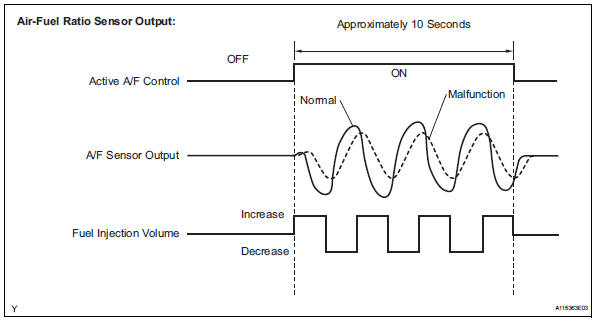
- Start the engine and warm it up.
- Drive the vehicle at a constant speed of between 40 km/h and 120 km/h (25 mph and 75 mph) for 3 minutes.
- Check the monitor result values on the intelligent tester by selecting the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / monitor info / test result.
- If the values indicated on the tester do not change, perform readiness monitor drive pattern for the a/f sensor and the heated oxygen sensor (see page es-19).
Hint:
Completion of all a/f sensor monitors is required to change the value in test result.
- Note the value of the monitor result.
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / dtc info / pending codes.
- Check if any dtcs (any pending dtcs) are set.
Monitor strategy
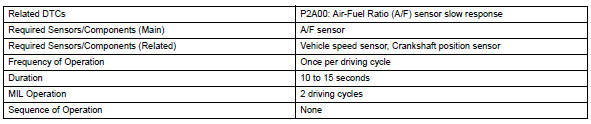
Typical enabling conditions
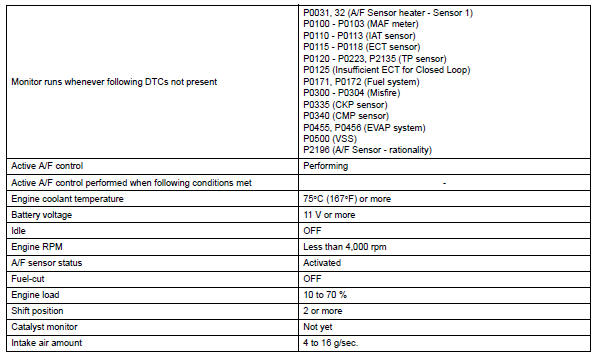
Typical malfunction thresholds
Monitor result
Refer to checking monitor status (see page es-17).
Wiring diagram
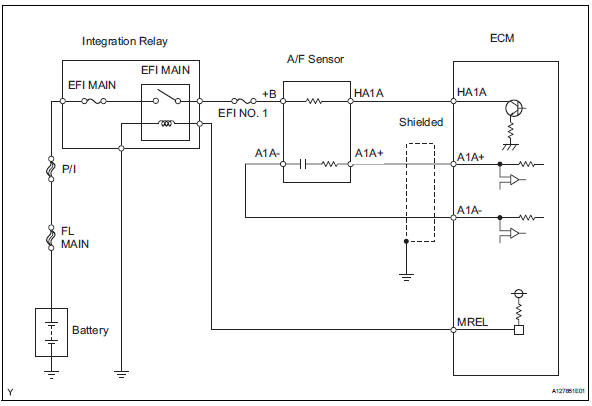
Inspection procedure
Hint:
Intelligent tester only: malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the a/f control function provided in the active test. The a/f control function can help to determine whether the air-fuel ratio (a/f) sensor, heated oxygen (ho2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
The following instructions describe how to conduct the a/f control operation using the intelligent tester.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Start the engine and turn the tester on.
- Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- On the tester, select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / active test / a/ f control
- Perform the a/f control operation with the engine idling (press the right or left button to change the fuel injection volume).
- Monitor the voltage outputs of the a/f and ho2 sensors (afs b1 s1 and o2s b1 s2) displayed on the tester.
Hint:
- The a/f control operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5 % Or increases the injection volume by 25 %.
- The sensors react in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
Standard
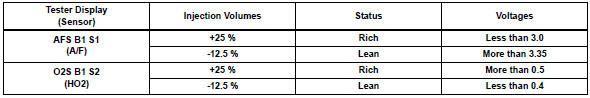
Notice:
The a/f sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the ho2 sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
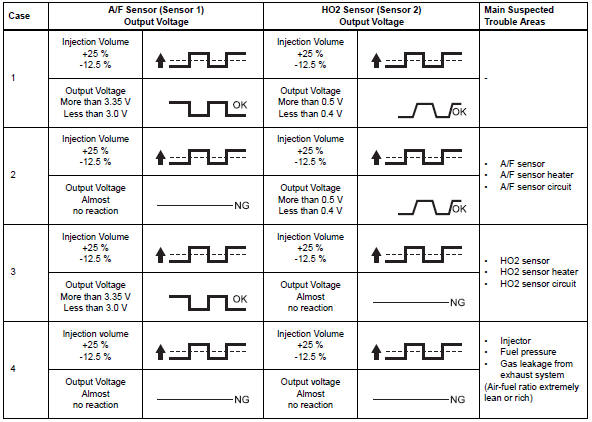
Following the a/f control procedure enables technicians to check and graph the voltage outputs of both the a/f and ho2 sensors.
To display the graph, select the following menu items on the tester: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / active test / a/f control / user data / afs b1 s1 and o2s b1 s2; and press the yes button and then the enter button followed by the f4 button.
Hint:
- Dtc p2a00 may be set when the air-fuel ratio is stuck rich or lean.
- A low a/f sensor voltage could be caused by a rich air-fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run rich.
- A high a/f sensor voltage could be caused by a lean air-fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run lean.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- Check any other dtcs output (in addition to dtc p2a00)
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Turn the ignition switch on.
- Turn the tester on.
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / dtc info / current codes.
- Read dtcs.
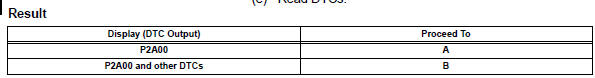
If any dtcs relating to the a/f sensor (dtcs for the a/f sensor heater or a/f sensor admittance) are output, troubleshoot those dtcs first.


- Inspect air-fuel ratio sensor (heater resistance) (see page es-83)


- Check harness and connector (ecm - air-fuel ratio sensor) (see page es- 310)


- Perform confirmation driving pattern

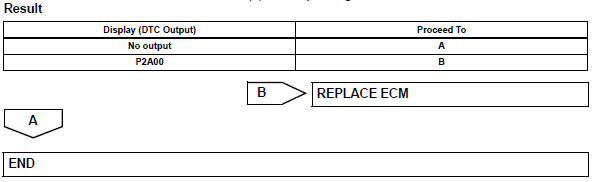
- Check whether dtc output recurs (dtc p2a00)
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Turn the ignition switch on and turn the tester on.
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / dtc info / pending codes.
- Read pending dtcs.
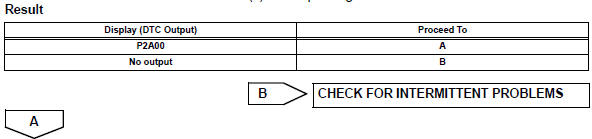
- Replace air-fuel ratio sensor

- Perform confirmation driving pattern

- Check whether dtc output recurs (dtc p2a00)
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Turn the ignition switch on and turn the tester on.
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / dtc info / pending codes.
- Read pending dtcs.
 Ecm / pcm internal engine off timer performance
Ecm / pcm internal engine off timer performance
Dtc summary
Description
To ensure the accuracy of the evap (evaporative emission) monitor values, the
soak timer, which is built
into the ecm, measures 5 hours (+-15 minutes) from when th ...
 Evap system
Evap system
Related dtcs
If any evap system dtcs are set, the malfunctioning area can be determined
using the table below.
Notice:
If the reference pressure difference between the first and second ch ...
Other materials:
Seat belt pretensioners (front seats)
The pretensioners help the seat
belts to quickly restrain the occupants
by retracting the seat belts
when the vehicle is subjected to
certain types of severe frontal or
side collision or a vehicle rollover.
The pretensioners do not activate
in the event of a minor frontal
impact, a minor ...
Problem symptoms table (2006/01- )
Hint:
Use the table below to help determine the cause of the
problem symptom. The potential causes of the symptoms are
listed in order of probability in the "suspected area" column
of the table. Check each symptom by checking the suspected
areas in the order they are listed. Replace p ...
Types of child restraints
Child restraint systems are classified into the following 3 types
according to the age and size of the child:
Rear facing „o infant seat/convertible
seat
Forward facing „o convertible
seat
Booster seat
Selecting an appropriate child restraint system
Use a child restraint ...
