Toyota RAV4 (XA40) 2013-2018 Service Manual: Mass or volume air flow circuit

Description
The mass air flow (maf) meter is a sensor that measures the amount of air flowing through the throttle valve.
The ecm uses this information to determine the fuel injection time and to provide the appropriate air-fuel ratio.
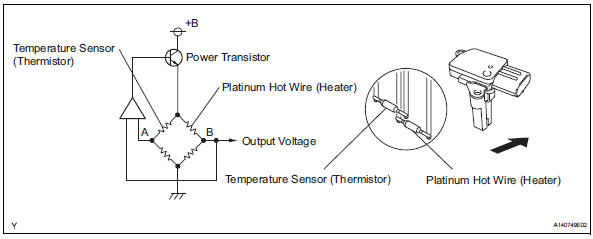
Inside the maf meter, there is a heated platinum wire which is exposed to the flow of intake air.
By applying a specific electrical current to the wire, the ecm heats it to a given temperature. The flow of incoming air cools both the wire and an internal thermistor, affecting their resistance. To maintain a constant current value, the ecm varies the voltage applied to these components in the maf meter. The voltage level is proportional to the airflow through the sensor, and the ecm uses it to calculate the intake air volume.
The circuit is constructed so that the platinum hot wire and the temperature sensor create a bridge circuit, and the power transistor is controlled so that the potentials of a and b remain equal to maintain the predetermined temperature.
Hint:
When any of these dtcs are set, the ecm enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ignition timing is calculated by the ecm, according to the engine rpm and throttle valve position. Fail-safe mode continues until a pass condition is detected.
Hint:
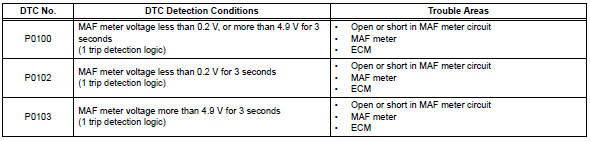
When any of these dtcs are set, check the air-flow rate by selecting the following menu items on the intelligent tester: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii/ data list / primary / maf.
Monitor description
If there is a defect in the maf meter or an open or short circuit, the voltage level deviates from the normal operating range. The ecm interprets this deviation as a malfunction in the maf meter and sets a dtc.
Example: when the sensor output voltage remains less than 0.2 V, or more than 4.9 V, for more than 3 seconds, the ecm sets a dtc.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a dtc is set 3 seconds after the engine is next started.
Monitor strategy
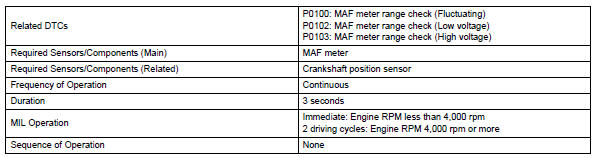
Typical enabling conditions
![]()
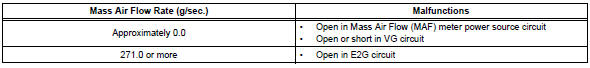
Typical malfunction thresholds
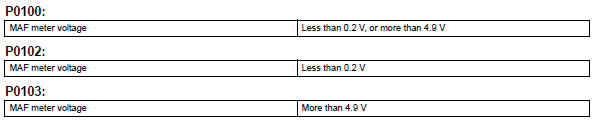
Component operating range
![]()
Wiring diagram
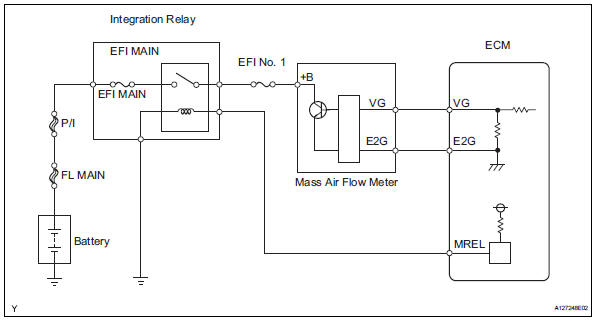
Inspection procedure
Hint:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
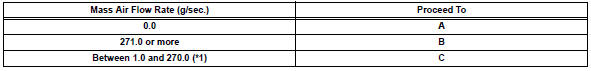
- Read value using intelligent tester (mass air flow rate)
- Connect the intelligent tester to the dlc3.
- Start the engine.
- Turn the tester on.
- Select the following menu items: diagnosis / enhanced obd ii / data list / primary / maf.
- Read the values displayed on the tester.
Result
Hint:
*1: The value must change when the throttle valve is
open or closed with the engine running.

- Inspect mass air flow meter (power source voltage)
- Disconnect the b1 mass air flow (maf) meter connector.
- Turn the ignition switch on.
- Measure the voltage between the terminal of the wire harness side connector and body ground.
Standard voltage 
- Reconnect the maf meter connector.
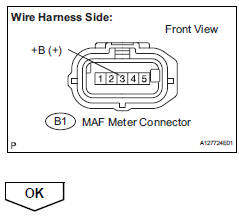

- Inspect mass air flow meter (vg voltage)
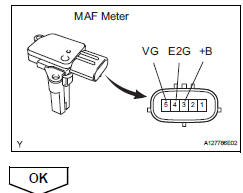
- Output voltage inspection.
- Apply battery voltage across terminals +b and e2g.
- Connect the positive (+) tester probe to terminal vg, and negative (-) tester probe to terminal e2g.
- Measure the voltage.
Standard voltage 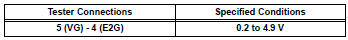

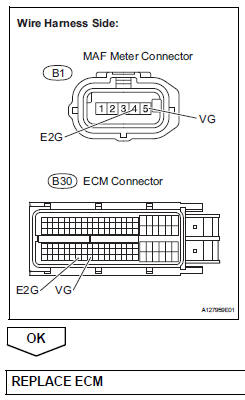
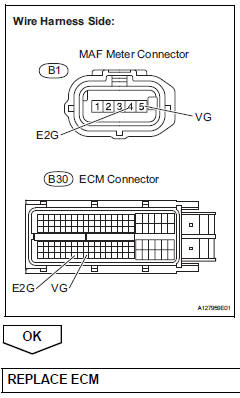
- Check harness and connector (mass air flow meter - ecm)
- Disconnect the b1 maf meter connector.
- Disconnect the b30 ecm connector.
- Measure the resistance.
Standard resistance (check for open)
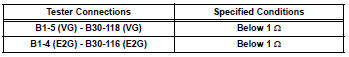
Standard resistance (check for short)

- Reconnect the maf meter connector.
- Reconnect the ecm connector.

Check harness and connector (mass air flow meter - integration relay)
- Check the efi no. 1 Fuse.
- Disconnect the b1 maf meter connector.
- Remove the integration relay from the engine room no. 1 Relay block.
- Check the resistance.
Standard resistance (check for open)
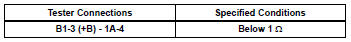
Standard resistance (check for short)

- Reconnect the maf meter connector.
- Reinstall the integration relay.
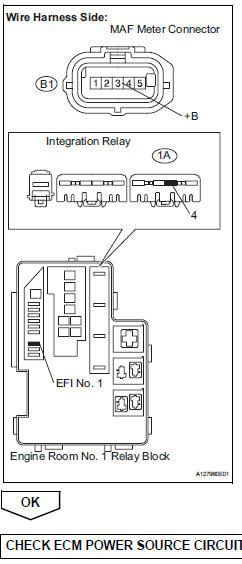

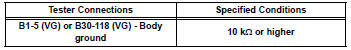
- Check harness and connector (sensor ground)
- Disconnect the b1 maf meter connector.
- Measure the resistance.

- Check harness and connector (mass air flow meter - ecm)
- Disconnect the b1 maf meter connector.
- Disconnect the b30 ecm connector.
- Measure the resistance.
Standard resistance (check for open)
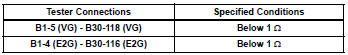
Standard resistance (check for short)
- Reconnect the maf meter connector.
- Reconnect the ecm connector.

 Oxygen (a/f) sensor heater control circuit
Oxygen (a/f) sensor heater control circuit
Hint:
Although the dtc titles say oxygen sensor, these dtcs relate to the
air-fuel ratio (a/f) sensor.
Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the three-way
catalytic convert ...
 Mass air flow circuit range / performance problem
Mass air flow circuit range / performance problem
Description
Refer to dtc p0100 (see page es-86).
Monitor description
The maf meter is a sensor that measures the amount of air flowing through the
throttle valve. The ecm
uses this infor ...
Other materials:
Steering wheel
Adjustment procedure
The steering wheel can be adjusted to a comfortable position.
Hold the steering wheel and
press the lever down.
Adjust to the ideal position by
moving the steering wheel horizontally
and vertically.
After adjustment, pull the lever up
to secure the steering ...
Disassembly
Remove radio setting condenser
Remove the bolt and condenser.
Remove oil pressure switch
Using a 24 mm deep socket wrench, remove the sensor.
Remove engine coolant temperature sensor
Using sst, remove the sensor and gasket.
Sst 09817-33190
Remove c ...
Reassembly
Hint:
When installing the ornament plate and emblem, heat the
radiator grille, ornament plate and emblem using a heat light.
Standard heating temperature
Notice:
Do not heat the radiator grille, ornament plate and
emblem excessively.
Install radiator grille emblem
Attach ...
